Chapter One Summary Introdutio to Reading and Writing Literature
Chapter 1: Introduction
Learning Objectives
At the conclusion of this affiliate, you volition be able to:
- Identify the purpose of the literature review in the research process
- Distinguish between different types of literature reviews
Pick upwardly nigh any book on research methods and you lot will observe a description of a literature review. At a basic level, the term implies a survey of factual or nonfiction books, articles, and other documents published on a particular bailiwick. Definitions may be similar across the disciplines, with new types and definitions continuing to emerge. Generally speaking, a literature review is a:
- "comprehensive background of the literature within the interested topic surface area…" (O'Gorman & MacIntosh, 2015, p. 31).
- "disquisitional component of the research procedure that provides an in-depth analysis of recently published research findings in specifically identified areas of interest." (House, 2018, p. 109).
- "written document that presents a logically argued case founded on a comprehensive understanding of the current country of knowledge nigh a topic of study" (Machi & McEvoy, 2012, p. 4).
As a foundation for knowledge advancement in every discipline, it is an important element of whatsoever research project. At the graduate or doctoral level, the literature review is an essential feature of thesis and dissertation, too as grant proposal writing. That is to say, "A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated enquiry…A researcher cannot perform pregnant enquiry without showtime agreement the literature in the field." (Boote & Beile, 2005, p. 3). It is by this means, that a researcher demonstrates familiarity with a body of knowledge and thereby establishes credibility with a reader. An advanced-level literature review shows how prior inquiry is linked to a new project, summarizing and synthesizing what is known while identifying gaps in the noesis base, facilitating theory development, closing areas where plenty research already exists, and uncovering areas where more research is needed. (Webster & Watson, 2002, p. thirteen)
A graduate-level literature review is a compilation of the most significant previously published research on your topic. Unlike an annotated bibliography or a research paper you may have written every bit an undergraduate, your literature review will outline, evaluate and synthesize relevant research and chronicle those sources to your ain thesis or inquiry question. It is much more than than a summary of all the related literature.
It is a type of writing that demonstrate the importance of your research by defining the main ideas and the human relationship between them. A skillful literature review lays the foundation for the importance of your stated problem and research question.
Literature reviews:
- define a concept
- map the research terrain or scope
- systemize relationships betwixt concepts
- identify gaps in the literature (Rocco & Plathotnik, 2009, p. 128)
The purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate that your inquiry question is meaningful. Additionally, you may review the literature of different disciplines to notice deeper meaning and understanding of your topic. It is especially important to consider other disciplines when you practice not find much on your topic in ane field of study. You will need to search the cognate literature before claiming there is "niggling previous research" on your topic.
Well developed literature reviews involve numerous steps and activities. The literature review is an iterative process considering you will do at least two of them: a preliminary search to larn what has been published in your area and whether there is sufficient support in the literature for moving alee with your subject. Afterward this outset exploration, you will bear a deeper dive into the literature to acquire everything you tin about the topic and its related issues.
Literature Review Tutorial

An effective literature review must:
- Methodologically analyze and synthesize quality literature on a topic
- Provide a business firm foundation to a topic or research area
- Provide a firm foundation for the selection of a research methodology
- Demonstrate that the proposed enquiry contributes something new to the overall torso of knowledge of advances the enquiry field'southward knowledge base of operations. (Levy & Ellis, 2006).
All literature reviews, whether they are qualitative, quantitative or both, will at some signal:
- Innovate the topic and ascertain its key terms
- Constitute the importance of the topic
- Provide an overview of the amount of available literature and its types (for case: theoretical, statistical, speculative)
- Identify gaps in the literature
- Point out consistent finding across studies
- Arrive at a synthesis that organizes what is known about a topic
- Discusses possible implications and directions for time to come research
In that location are many different types of literature reviews, withal at that place are some shared characteristics or features. Recollect a comprehensive literature review is, at its virtually key level, an original piece of work based on an extensive disquisitional examination and synthesis of the relevant literature on a topic. Equally a written report of the research on a particular topic, information technology is arranged by key themes or findings, which may lead upward to or link to the research question. In some cases, the enquiry question will drive the type of literature review that is undertaken.
The post-obit section includes brief descriptions of the terms used to draw dissimilar literature review types with examples of each. The included citations are open up admission, Artistic Commons licensed or copyright-restricted.
1.3.1 Types of Review
1.three.1.one Conceptual
Guided by an understanding of basic issues rather than a research methodology. You are looking for cardinal factors, concepts or variables and the presumed relationship between them. The goal of the conceptual literature review is to categorize and describe concepts relevant to your written report or topic and outline a relationship between them. You lot volition include relevant theory and empirical research.
Examples of a Conceptual Review:
- Instruction: The formality of learning science in everyday life: A conceptual literature review. (Dohn, 2010).
- Instruction: Are we asking the right questions? A conceptual review of the educational development literature in college education. (Amundsen & Wilson, 2012).
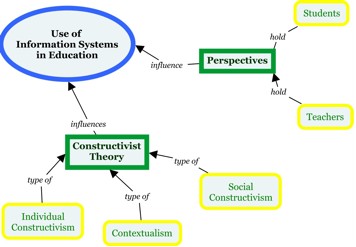
1.3.ane.2 Empirical
An empirical literature review collects, creates, arranges, and analyzes numeric data reflecting the frequency of themes, topics, authors and/or methods found in existing literature. Empirical literature reviews nowadays their summaries in quantifiable terms using descriptive and inferential statistics.
Examples of an Empirical Review:
- Nursing: False-positive findings in Cochrane meta-analyses with and without application of trial sequential analysis: An empirical review. (Imberger, Thorlund, Gluud, & Wettersley, 2016).
- Instruction: Impediments of e-learning adoption in higher learning institutions of Tanzania: An empirical review (Mwakyusa & Mwalyagile, 2016).
1.3.1.3 Exploratory
Unlike a synoptic literature review, the purpose here is to provide a broad arroyo to the topic surface area. The aim is breadth rather than depth and to become a general feel for the size of the topic area. A graduate pupil might practice an exploratory review of the literature before beginning a synoptic, or more than comprehensive ane.
Examples of an Exploratory Review:
- Education: University research management: An exploratory literature review. (Schuetzenmeister, 2010).
- Pedagogy: An exploratory review of design principles in constructivist gaming learning environments. (Rosario & Widmeyer, 2009).

1.iii.1.4 Focused
A type of literature review limited to a single attribute of previous research, such as methodology. A focused literature review generally will describe the implications of choosing a particular element of past inquiry, such as methodology in terms of data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Examples of a Focused Review:
- Nursing: Clinical inertia in the management of blazon two diabetes mellitus: A focused literature review. (Khunti, Davies, & Khunti, 2015).
- Teaching: Language sensation: Genre awareness-a focused review of the literature. (Stainton, 1992).
ane.3.1.5 Integrative
Critiques by research and draws overall conclusions from the body of literature at a specified point in time. Reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way. Most integrative reviews are intended to address mature topics or emerging topics. May require the author to adopt a guiding theory, a set of competing models, or a bespeak of view virtually a topic. For more clarification of integrative reviews, see Whittemore & Knafl (2005).
Examples of an Integrative Review:
- Nursing: Interprofessional teamwork and collaboration betwixt community health workers and healthcare teams: An integrative review. (Franklin, Bernhardt, Lopez, Long-Middleton, & Davis, 2015).
- Didactics: Exploring the gap between teacher certification and permanent employment in Ontario: An integrative literature review. (Brock & Ryan, 2016).
1.3.1.6 Meta-analysis
A subset of a systematic review, that takes findings from several studies on the same subject and analyzes them using standardized statistical procedures to pool together information. Integrates findings from a large torso of quantitative findings to enhance understanding, describe conclusions, and detect patterns and relationships. Gather data from many different, contained studies that look at the same research question and appraise similar result measures. Information is combined and re-analyzed, providing a greater statistical power than whatever unmarried report alone. It'southward important to note that not every systematic review includes a meta-assay but a meta-analysis can't exist without a systematic review of the literature.
Examples of a Meta-Assay:
- Education: Efficacy of the cooperative learning method on mathematics achievement and attitude: A meta-assay research. (Capar & Tarim, 2015).
- Nursing: A meta-assay of the effects of non-traditional teaching methods on the critical thinking abilities of nursing students. (Lee, Lee, Gong, Bae, & Choi, 2016).
- Education: Gender differences in student attitudes toward science: A meta-assay of the literature from 1970 to 1991. (Weinburgh, 1995).
1.3.1.7 Narrative/Traditional
An overview of research on a detail topic that critiques and summarizes a trunk of literature. Typically broad in focus. Relevant past inquiry is selected and synthesized into a coherent discussion. Methodologies, findings and limits of the existing body of knowledge are discussed in narrative grade. Sometimes also referred to as a traditional literature review. Requires a sufficiently focused research question. The procedure may be field of study to bias that supports the researcher'due south own work.
Examples of a Narrative/Traditional Review:
- Nursing: Family carers providing support to a person dying in the dwelling setting: A narrative literature review. (Morris, Rex, Turner, & Payne, 2015).
- Pedagogy: Take chances pedagogy and Outward Spring: Out-of-class experiences that make a lasting deviation. (Hattie, Marsh, Neill, & Richards, 1997).
- Education: Good quality give-and-take is necessary only not sufficient in asynchronous tuition: A brief narrative review of the literature. (Fear & Erikson-Chocolate-brown, 2014).
- Nursing: Outcomes of physician job satisfaction: A narrative review, implications, and directions for future inquiry. (Williams & Skinner, 2003).
1.3.1.8 Realist
Aspecific type of literature review that is theory-driven and interpretative and is intended to explicate the outcomes of a complex intervention program(s).
Examples of a Realist Review:
- Nursing: Lean thinking in healthcare: A realist review of the literature. (Mazzacato, Savage, Brommels, 2010).
- Education: Unravelling quality civilization in college education: A realist review. (Bendermacher, Egbrink, Wolfhagen, & Dolmans, 2017).
one.3.i.ix Scoping
Tend to exist non-systematic and focus on breadth of coverage conducted on a topic rather than depth. Apply a broad range of materials; may not evaluate the quality of the studies as much as count the number. One means of understanding existing literature. Aims to identify nature and extent of research; preliminary assessment of size and scope of bachelor research on topic. May include enquiry in progress.
Examples of a Scoping Review:
- Nursing: Organizational interventions improving access to community-based primary health treat vulnerable populations: A scoping review. (Khanassov, Pluye, Descoteaux, Haggerty, Russell, Gunn, & Levesque, 2016).
- Education: Interdisciplinary doctoral research supervision: A scoping review. (Vanstone, Hibbert, Kinsella, McKenzie, Pitman, & Lingard, 2013).
- Nursing: A scoping review of the literature on the abolition of user fees in health intendance services in Africa. (Ridde, & Morestin, 2011).
1.iii.i.ten Synoptic
Unlike an exploratory review, the purpose is to provide a curtailed just accurate overview of all textile that appears to be relevant to a called topic. Both content and methodological material is included. The review should aim to be both descriptive and evaluative. Summarizes previous studies while also showing how the trunk of literature could exist extended and improved in terms of content and method by identifying gaps.
Examples of a Synoptic Review:
- Educational activity: Theoretical framework for educational assessment: A synoptic review. (Ghaicha, 2016).
- Education: School effects research: A synoptic review of past efforts and some suggestions for the time to come. (Cuttance, 1981).
i.iii.1.11 Systematic Review
A rigorous review that follows a strict methodology designed with a presupposed selection of literature reviewed. Undertaken to clarify the land of existing research, the testify, and possible implications that tin be drawn from that. Using comprehensive and exhaustive searching of the published and unpublished literature, searching various databases, reports, and gray literature. Transparent and reproducible in reporting details of time frame, search and methods to minimize bias. Must include a team of at least ii-3 and includes the critical appraisal of the literature. For more description of systematic reviews, including links to protocols, checklists, workflow processes, and structure see "A Young Researcher's Guide to a Systematic Review".
Examples of a Systematic Review:
- Instruction: The potentials of using deject computing in schools: A systematic literature review (Hartmann, Braae, Pedersen, & Khalid, 2017)
- Nursing: Is butter back? A systematic review and meta-assay of butter consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and total mortality. (Pimpin, Wu, Haskelberg, Del Gobbo, & Mozaffarian, 2016).
- Didactics: The employ of research to better professional person exercise: a systematic review of the literature. (Hemsley-Brown & Sharp, 2003).
- Nursing: Using computers to self-manage blazon 2 diabetes. (Pal, Eastwood, Michie, Farmer, Barnard, Peacock, Forest, Inniss, & Murray, 2013).
i.3.1.12 Umbrella/Overview of Reviews
Compiles evidence from multiple systematic reviews into one document. Focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address those interventions and their effects. Often used in recommendations for exercise.
Examples of an Umbrella/Overview Review:
- Education: Reflective practice in healthcare education: An umbrella review. (Fragknos, 2016).
- Nursing: Systematic reviews of psychosocial interventions for autism: an umbrella review. (Seida, Ospina, Karkhaneh, Hartling, Smith, & Clark, 2009).
For a brief discussion see "Not all literature reviews are the aforementioned" (Thomson, 2013).
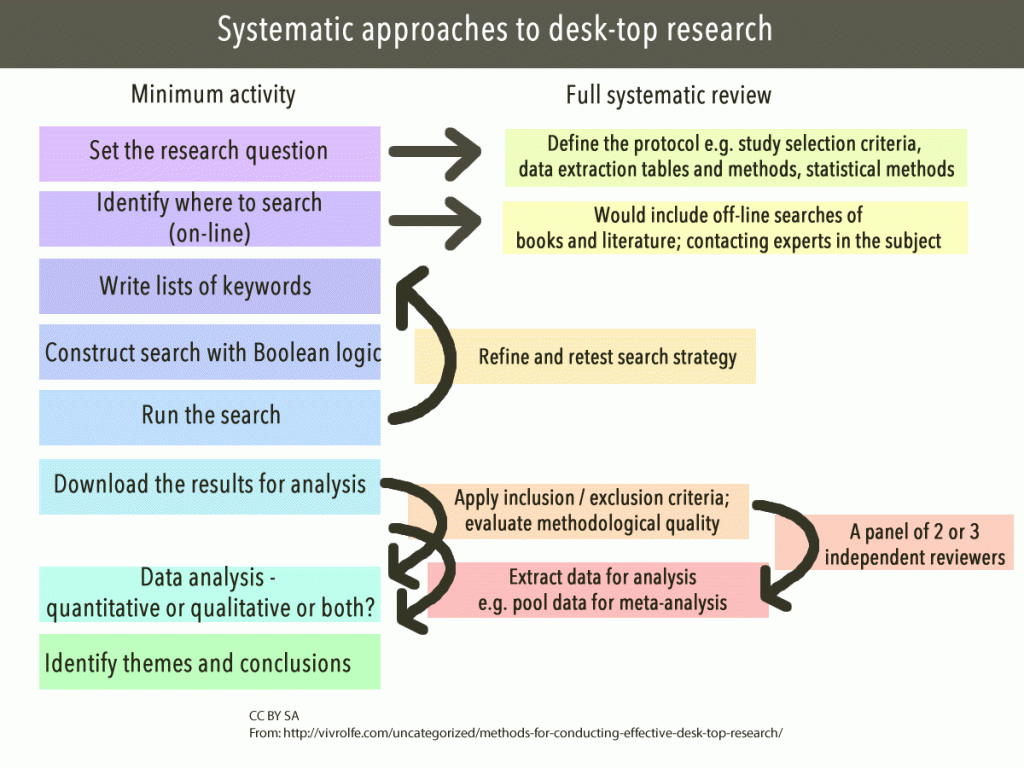
The purpose of the literature review is the same regardless of the topic or research method. It tests your ain research question against what is already known about the subject.
one.four.1 Start – It's part of the whole. Omission of a literature review affiliate or department in a graduate-level project represents a serious void or absence of critical element in the research process.
The upshot of your review is expected to demonstrate that you:
- can systematically explore the research in your topic area
- tin read and critically analyze the literature in your subject field and so utilize it accordingly to advance your ain work
- accept sufficient knowledge in the topic to undertake further investigation
1.4.2 Second – Information technology'south healthy!
- Yous improve your skills every bit a researcher
- You lot become familiar with the soapbox of your bailiwick and learn how to be a scholar in your field
- Y'all learn through writing your ideas and finding your phonation in your discipline surface area
- Yous define, redefine and clarify your enquiry question for yourself in the process
1.four.3 Third – Information technology's good for your reader. Your reader expects yous to accept done the difficult work of gathering, evaluating and synthesizes the literature. When y'all do a literature review you:
- Set the context for the topic and nowadays its significance
- Identify what'southward of import to know near your topic – including individual cloth, prior research, publications, organizations and authors.
- Demonstrate relationships among prior research
- Establish limitations of existing knowledge
- Analyze trends in the topic'due south treatment and gaps in the literature
1.4.4 Why do a literature review?
- To locate gaps in the literature of your subject
- To avert reinventing the wheel
- To conduct on where others have already been
- To identify other people working in the aforementioned field
- To increase your latitude of knowledge in your field of study area
- To find the seminal works in your field
- To provide intellectual context for your own piece of work
- To acknowledge opposing viewpoints
- To put your work in perspective
- To demonstrate you can detect and recall previous piece of work in the area
Graduate-level literature reviews are more than a summary of the publications you find on a topic. Equally you have seen in this brief introduction, literature reviews are a very specific type of inquiry, analysis, and writing. Nosotros will explore these topics more than in the next chapters. Some things to keep in mind as you begin your ain enquiry and writing are means to avoid the most common errors seen in the first try at a literature review. For a quick review of some of the pitfalls and challenges a new researcher faces when he/she begins piece of work, run into "Get Ready: Academic Writing, Full general Pitfalls and (oh yes) Getting Started!".
As yous begin your own graduate-level literature review, endeavor to avoid these mutual mistakes:
- Accepts some other researcher's finding as valid without evaluating methodology and information
- Contrary findings and alternative interpretations are non considered or mentioned
- Findings are not conspicuously related to one'south own written report, or findings are too general
- Insufficient time allowed to define all-time search strategies and writing
- Isolated statistical results are simply reported rather than synthesizing the results
- Issues with selecting and using virtually relevant keywords, discipline headings and descriptors
- Relies too heavily on secondary sources
- Search methods are not recorded or reported for transparency
- Summarizes rather than synthesizes manufactures
In conclusion, the purpose of a literature review is three-fold:
- to survey the electric current state of noesis or evidence in the area of inquiry,
- to place key authors, articles, theories, and findings in that area, and
- to identify gaps in noesis in that inquiry expanse.
A literature review is commonly washed today using computerized keyword searches in online databases, oftentimes working with a trained librarian or information skilful. Keywords can be combined using the Boolean operators, "and", "or" and sometimes "non" to narrow downward or expand the search results. In one case a listing of articles is generated from the keyword and subject heading search, the researcher must then manually browse through each title and abstruse, to determine the suitability of that article before a total-text article is obtained for the enquiry question.
Literature reviews should be reasonably complete, and not restricted to a few journals, a few years, or a specific methodology or research design. Reviewed articles may be summarized in the course of tables, and can exist farther structured using organizing frameworks such every bit a concept matrix.
A well-conducted literature review should point whether the initial research questions accept already been addressed in the literature, whether there are newer or more interesting research questions available, and whether the original research questions should be modified or inverse in light of findings of the literature review.
The review tin as well provide some intuitions or potential answers to the questions of involvement and/or help place theories that take previously been used to address similar questions and may provide prove to inform policy or conclusion-making. (Bhattacherjee, 2012).

Do
Read Abstruse ane. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of literature review exercise you call up this study is and why? See the Respond Central for the correct response.
Nursing: To describe evidence of international literature on the safe care of the hospitalised child after the World Alliance for Patient Condom and list contributions of the general theoretical framework of patient safety for paediatric nursing.
An integrative literature review between 2004 and 2015 using the databases PubMed, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Wellness Literature (CINAHL), Scopus, Web of Science and Wiley Online Library, and the descriptors Safety or Patient safety, Hospitalised child, Paediatric nursing, and Nursing care.
Xxx-2 manufactures were analysed, most of which were from Due north American, with a descriptive approach. The quality of the recorded information in the medical records, the utilize of checklists, and the training of wellness workers contribute to safety care in paediatric nursing and improve the medication process and partnerships with parents.
General data available on patient condom should exist incorporated in paediatric nursing care. (Wegner, Silva, Peres, Bandeira, Frantz, Botene, & Predebon, 2017).
Read Abstruse ii. Refer to Types of Literature Reviews. What type of lit review do you lot think this written report is and why? See the Answer Primal for the correct response.
Education: The focus of this newspaper centers around timing associated with early childhood education programs and interventions using meta-analytic methods. At any given assessment age, a child's current age equals starting historic period, plus duration of program, plus years since program ended. Variability in cess ages across the studies should enable everyone to identify the separate furnishings of all three fourth dimension-related components. The projection is a meta-analysis of evaluation studies of early childhood education programs conducted in the United states and its territories between 1960 and 2007. The population of involvement is children enrolled in early babyhood instruction programs between the ages of 0 and 5 and their control-group counterparts. Since the information come from a meta-analysis, the population for this study is drawn from many dissimilar studies with diverse samples. Given the preliminary nature of their analysis, the authors cannot offer conclusions at this signal. (Duncan, Leak, Li, Magnuson, Schindler, & Yoshikawa, 2011).
Test Yourself
Encounter Answer Key for the correct responses.
Question i
The purpose of a graduate-level literature review is to summarize in as many words equally possible everything that is known about my topic.
- Truthful
- False
Question 2
A literature review is significant because in the process of doing ane, the researcher learns to read and critically assess the literature of a subject field and then uses information technology appropriately to advance his/her own research.
- True
- False
Question iii
Read the following abstract and choose the correct blazon of literature review it represents.
Nursing: Eastward-cigarette utilise has go increasingly pop, especially among the immature. Its long-term influence upon health is unknown. Aim of this review has been to present the current state of cognition about the touch on of east-cigarette use on health, with an accent on Fundamental and Eastern Europe. During the preparation of this narrative review, the literature on e-cigarettes available within the network PubMed was retrieved and examined. In the final review, 64 enquiry papers were included. Nosotros specifically assessed the construction and operation of the e-cigarette too as the chemic composition of the e-liquid; the impact that vapor arising from the use of e-cigarette explored in experimental models in vitro; and short-term effects of utilise of e-cigarettes on users' health. Among the substances inhaled past the east-smoker, there are several harmful products, such as: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acroleine, propanal, nicotine, acetone, o-methyl-benzaldehyde, carcinogenic nitrosamines. Results from experimental animal studies indicate the negative bear upon of e-cigarette exposure on exam models, such as ascytotoxicity, oxidative stress, inflammation, airway hyper reactivity, airway remodeling, mucin production, apoptosis, and emphysematous changes. The curt-term impact of e-cigarettes on human being wellness has been studied generally in experimental setting. Available evidence shows that the use of east-cigarettes may upshot in acute lung function responses (eastward.g., increase in impedance, peripheral airway menstruation resistance) and induce oxidative stress. Based on the current available show, eastward-cigarette use is associated with harmful biologic responses, although it may exist less harmful than traditional cigarettes. (Jankowski, Brożek, Lawson, Skoczyński, & Zejda, 2017).
- Meta-analysis
- Exploratory
- Narrative
- Empirical
Question four
Read the following abstract and choose the correct type of literature review it represents.
Educational activity: In this review, Mary Vorsino writes that she is interested in keeping the potential influences of women pragmatists of Dewey's mean solar day in mind while presenting modernistic feminist re readings of Dewey. She wishes to construct a narrowly-focused and succinct literature review of thinkers who have donned a feminist lens to clarify Dewey's approaches to teaching, learning, and republic and to utilise Dewey's works in theorizing on gender and education and on gender in society. This article beginning explores Dewey as both an ally and a problematic figure in feminist literature and and so investigates the broader sphere of feminist pragmatism and two primal themes within it: (i) valuing diversity, and various experiences; and (ii) problematizing stock-still truths. (Vorsino, 2015).
- Scoping
- Exploratory
- Synoptic
- Focused
Chapter One Summary Introdutio to Reading and Writing Literature
Source: https://press.rebus.community/literaturereviewsedunursing/chapter/chapter-1/
0 Response to "Chapter One Summary Introdutio to Reading and Writing Literature"
Post a Comment